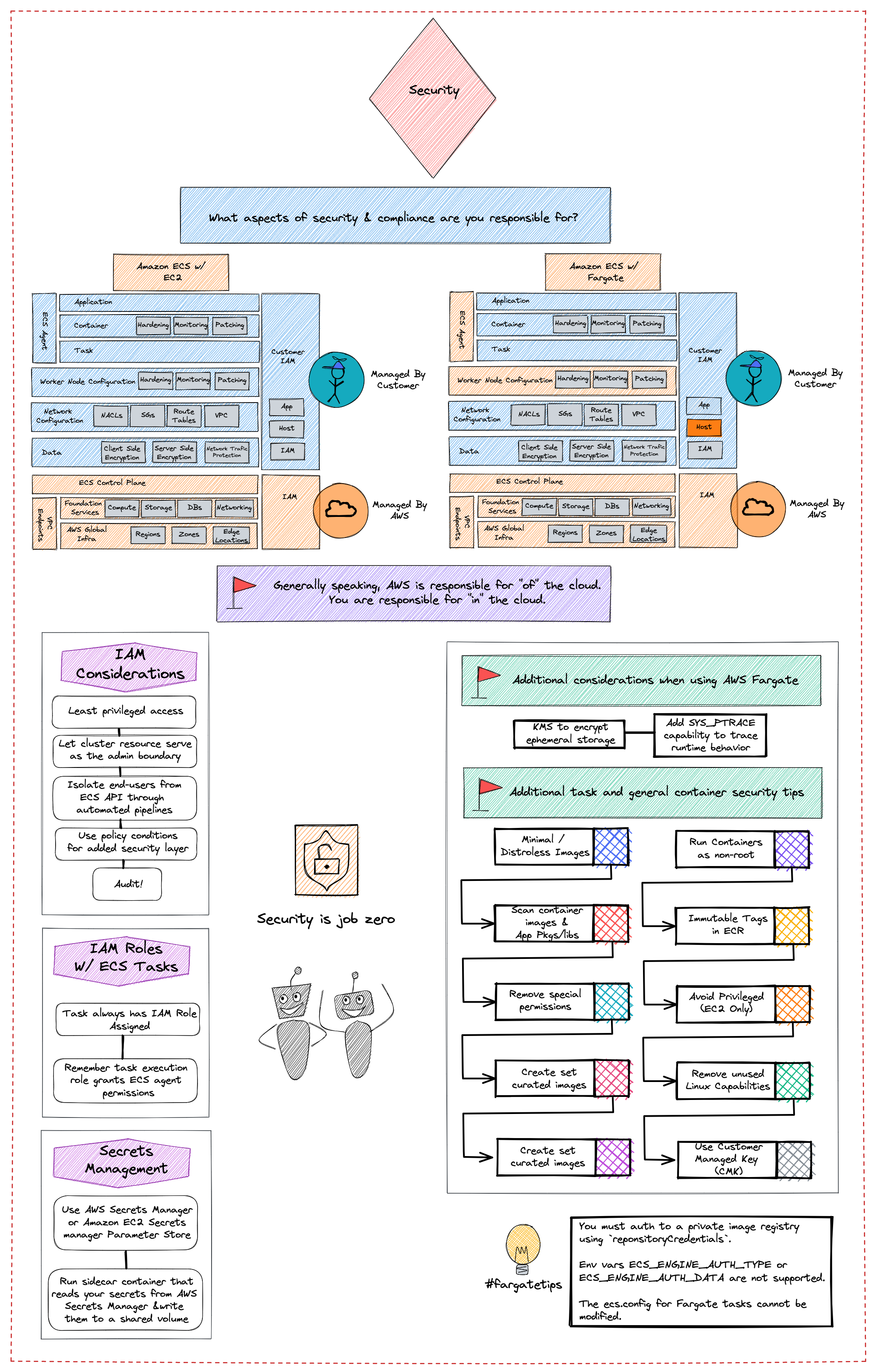
Container Platform Best Practices: Security
This visual provides security and compliance recommendations for protecting your information, systems, and other assets that are reliant on Amazon ECS. It also introduces some risk assessments and mitigation strategies that you can use to have a better grip on the security controls that are built for Amazon ECS clusters and the workloads that they support. Each topic in this guide starts with a brief overview, followed by a list of recommendations and best practices that you can use to secure your Amazon ECS clusters.
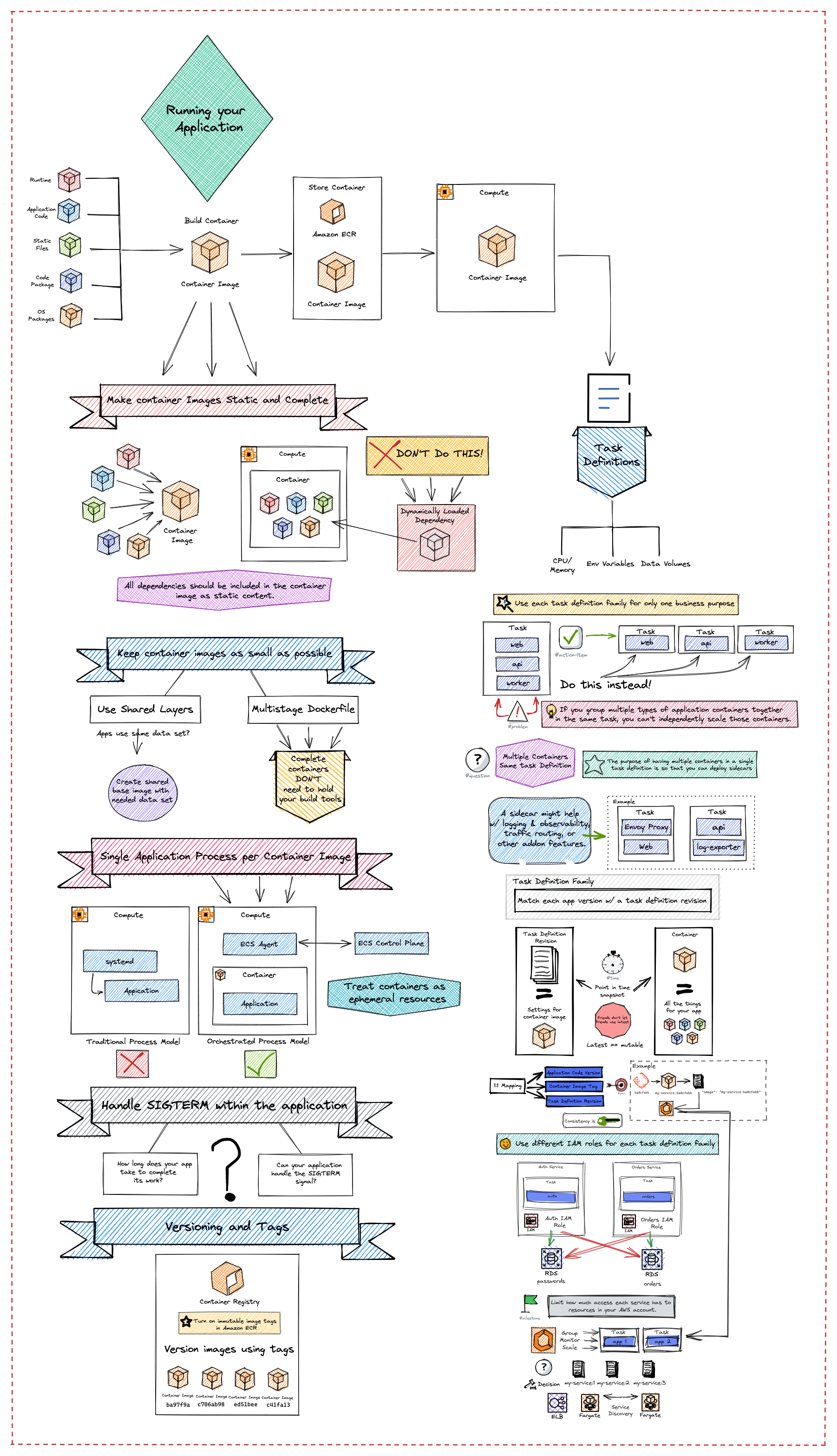
Container Platform Best Practices: Running Your App
Before you run an application using Amazon Elastic Container Service, make sure that you understand how the various aspects of your application work with features in Amazon ECS. This visual covers the main Amazon ECS resources types, what they’re used for, and best practices for using each of these resource types.
EC2 or AWS Fargate?
There are two main compute options for running containers with Amazon Elastic Container Service:
- EC2 (Deploy and manage your own cluster of self managed virtual machine instances that can each run one or more containers)
- AWS Fargate (Run containers directly, without any virtual machines to think about)
Both are completely valid techniques for operating your containers in a scalable and reliable fashion. Which one you pick depends on which factors you want to optimize for.